ニューラルネット実装
今回やったこと:
- 入力: 正弦波(
)を学習させて、-1 - 1 までの整数食わしたら
を返す
- 中間層: シグモイド関数(3 個)
- 出力層: 恒等関数
- 損失関数: 二乗和誤差
- 最適化アルゴリズム: 勾配降下法
- バッチサイズ: 1
で実装する。
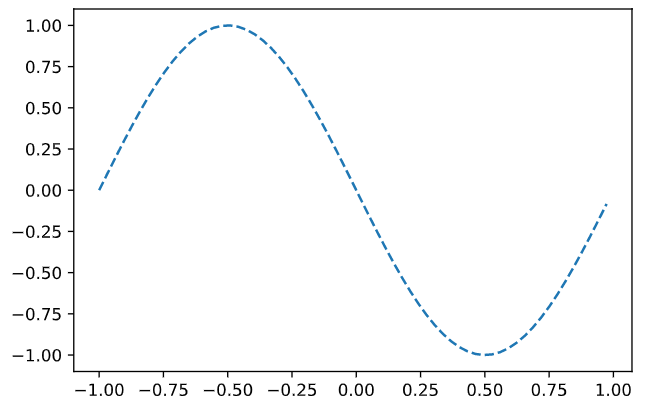
まずは学習データその他
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt %matplotlib inline wb_width = 0.01 # 重みバイアスの広がり方 epoch = 2001 # 学習データ数 eta = 0.1 # 学習係数 input_data = np.arange(0, np.pi * 2, 0.1) # 学習データ correct_data = np.sin(input_data) # 正解データ input_data = (input_data - np.pi) / np.pi # -1 - 1 にデータを整形 n_data = len(correct_data) # データ数 # 各層のニューロン数 n_in = 1 n_mid = 3 n_out = 1 # 学習データのプロット plt.plot(input_data, correct_data) plt.show()
出力層の勾配を考える。参考は 前回の記事 でやったやつ。
二乗和誤差と恒等関数の組み合わせだと、 の値は
で、残りのパラメータは
class Neuron: def __init__(self, n_upper, n, activation_function, differential_function): self.w = wb_width * np.random.randn(n_upper, n) self.b = wb_width * np.random.randn(n) self.grad_w = np.zeros((n_upper, n)) self.grad_b = np.zeros((n)) self.activation_function = activation_function self.differential_function = differential_function def update(self, eta): self.w -= eta * self.grad_w self.b -= eta * self.grad_b def forward(self, x): self.x = x u = x.dot(self.w) + self.b self.y = self.activation_function(u) return self.y def backword(self, t): delta = self.differential_function(self.y, t) self.grad_w = self.x.T.dot(delta) self.grad_b = np.sum(delta, axis=0) self.grad_x = delta.dot(self.w.T) return self.grad_x def identity_func(u): """恒等関数""" return u def differential_output(y, t): """恒等関数+二乗和誤差の微分""" return y - t class Output(Neuron): pass
重みとバイアスは共通の作りなので、Neuron として独立。
forward で順伝播したときに、それぞれの値をクラス内変数に格納する。
backword で格納した値と、目標値 を受け取って勾配を作る。
中間層はシグモイド関数。
こっちはこんな感じ
def sigmoid(u): """シグモイド関数""" return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-u)) def differential_sigmod(grad_y, y): """シグモイド関数の微分関数""" return grad_y * (1 - y) * y class Middle(Neuron): def backword(self, grad_y): delta = self.differential_function(grad_y, self.y) self.grad_w = self.x.T.dot(delta) self.grad_b = delta.sum(axis = 0) self.grad_x = delta.dot(self.w.T) return self.grad_x
ということで実際に学習させてみる
middle_layer: Middle = Middle(n_in, n_mid, sigmoid, differential_sigmod) output_layer: Output = Output(n_mid, n_out, identity_func, differential_output) # 途中経過の表示間隔 interval = 200 for i in range(epoch): # 学習データのシャッフル index_random = np.arange(n_data) np.random.shuffle(index_random) # 学習状況の把握用 total_err = 0 plot_x = [] plot_y = [] for idx in index_random: # ランダムに取り出した x とそれの対となる sin(x) の値を取得 x = input_data[idx:idx+1] t = correct_data[idx:idx+1] # 順伝播させて y = output_layer.forward( middle_layer.forward(x.reshape(1, 1))) # 逆伝播(正式解を与えて勾配計算させ) middle_layer.backword( output_layer.backword(t.reshape(1, 1))) # 重み+バイアス更新 middle_layer.update(eta) output_layer.update(eta) if i % interval == 0: # 二乗和誤差の計算(y = 出力層の結果, t = 正解値) total_err += 1.0 / 2.0 * np.sum(np.square(y - t)) # 出力の記録 plot_x.append(x) plot_y.append(y) if i % interval == 0: # 出力のグラフ表示 plt.plot(input_data, correct_data, linestyle = 'dashed') plt.scatter(plot_x, plot_y, marker='o') plt.show() print('Epoch:' + str(i) + '/' + str(epoch), 'Error:' + str(total_err / n_data))
1 回目(学習前)
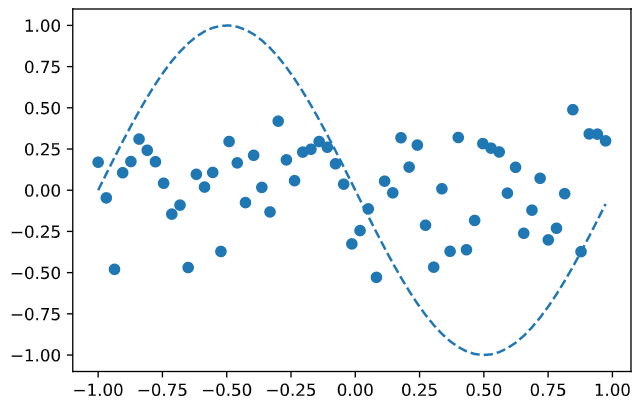
200 回学習

400 回学習

飛んで 1000 回学習

2000 回学習時点

ということで、「この時はこの値を返す」みたいなことを学習させることができたと。